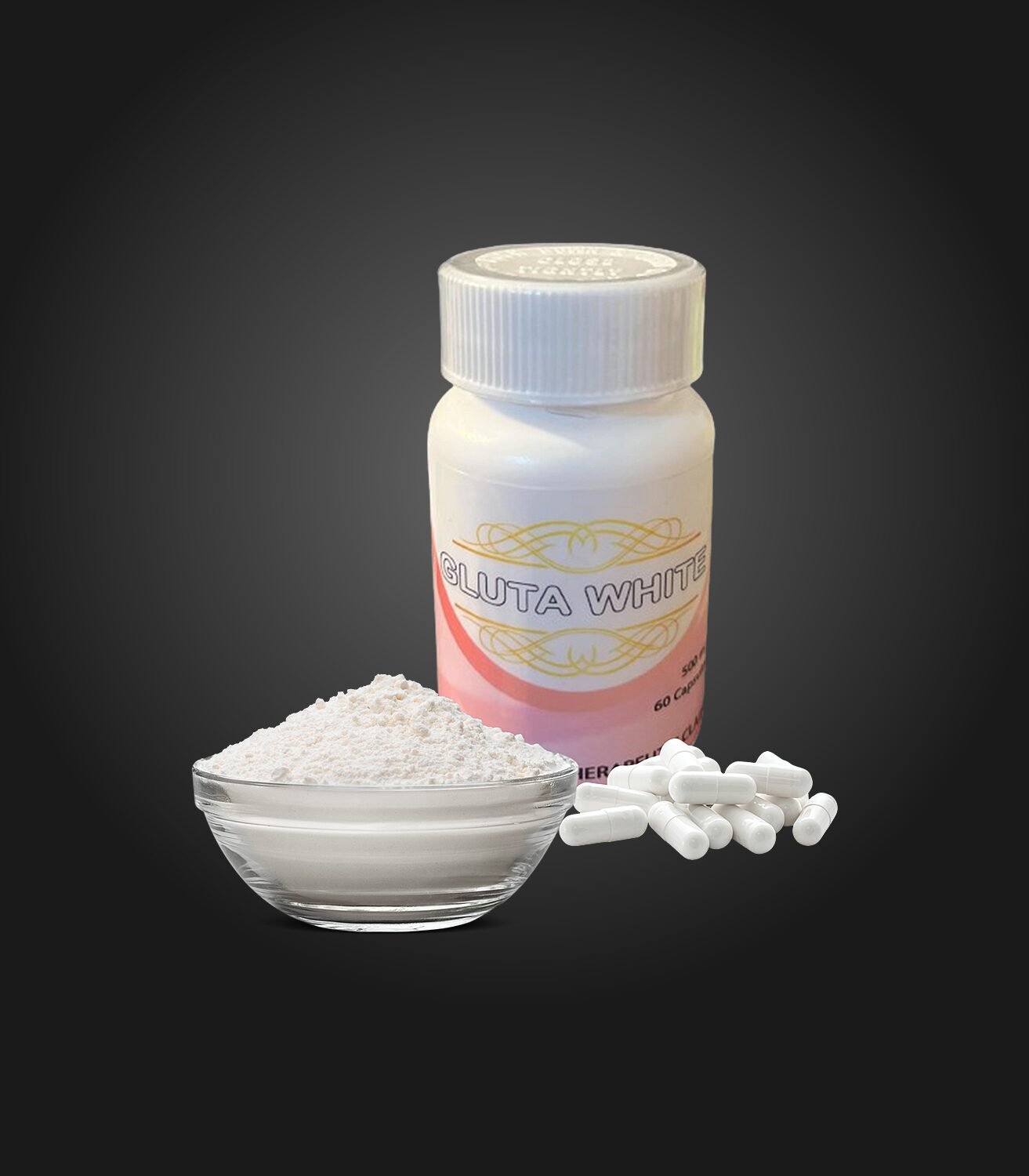
Glutawhite
₱999.00
Taking glutathione capsules can boost antioxidant defenses, improve skin health, and support detoxification processes in the body.
Ingredients: L-Glutathione, Collagen, Alpha Lipoic Acid, Vitamin E, Sodium Ascorbate, Zinc
99 in stock (can be backordered)
Glutathione is a tripeptide molecule composed of three amino acids: cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine. It is a crucial antioxidant that plays a vital role in various biological processes within the human body. The primary function of glutathione is to protect cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals and reactive oxygen species.
Key functions of glutathione include:
Antioxidant Defense: Glutathione helps neutralize free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and various diseases.
Detoxification: It plays a critical role in the detoxification of harmful substances, such as heavy metals and certain drugs, by binding to them and facilitating their elimination from the body.
Immune System Support: Glutathione is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system. It helps regulate the activity of immune cells and is involved in the proliferation and activation of lymphocytes.
Cellular Repair: It is involved in the repair of damaged DNA and protein molecules, contributing to the overall maintenance of cellular health.
Reduction of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): Glutathione participates in enzymatic reactions that convert harmful reactive oxygen species into less harmful substances, preventing cellular damage.
The body naturally produces glutathione, and it can also be obtained through certain foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and meats. Additionally, glutathione supplements are available, but their effectiveness can be influenced by factors such as absorption and metabolism.
Because of its critical role in maintaining cellular health, glutathione has been studied in various medical conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and immune disorders. However, more research is needed to fully understand its impact on these conditions and the potential benefits of supplementation.